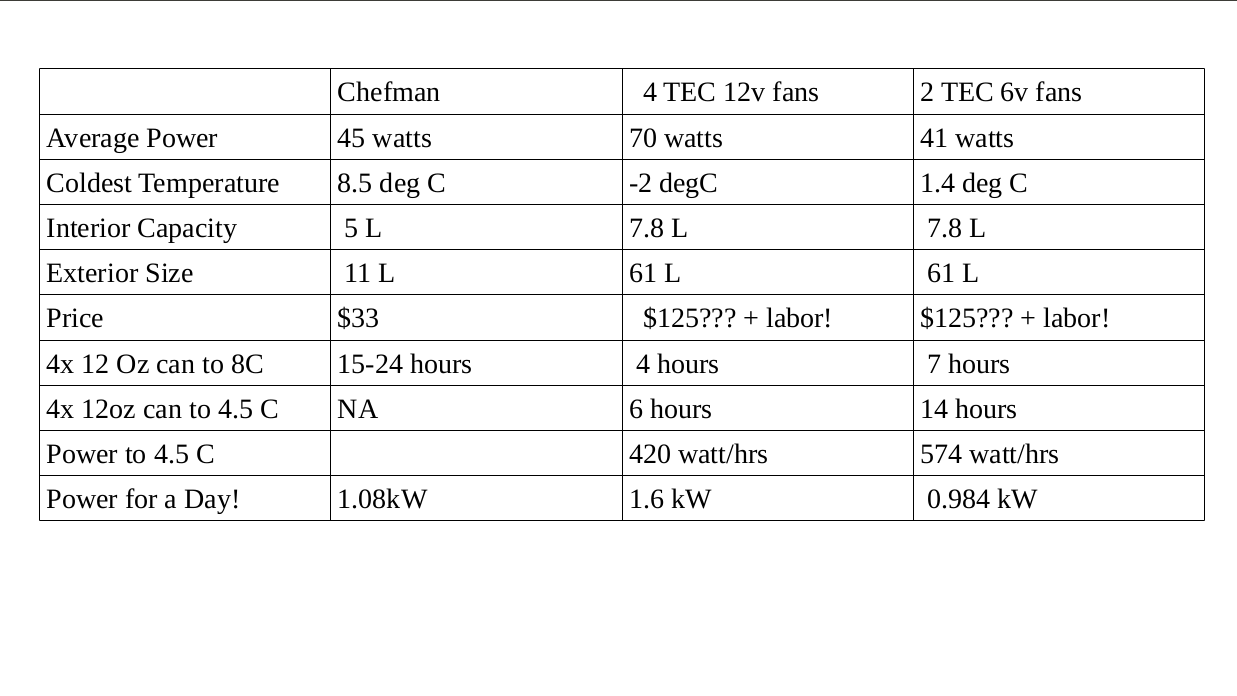
My DIY TEC Cooler has an interior volume of 480 cubic inches (6x8x10) and an interior surface area of 376 square inches (2.61 sq ft). It has an exterior volume of 1.55 cubic feet (12x14x16) and an exterior surface area of 1168 square inches (8.11 sq ft). It generally has 3 layers of 3/4″ poly-iso insulation (R5) plus a small amount of one-part urethane expanding foam (say, R2?) in some areas, for an estimated R 17 insulation value (sorry, I’m using imperial units here as my insulation comes with R values….)
To calculate the amount of heat that will escape from inside my cooler to the outside (the amount of heat loss I need to counteract with the TEC system to maintain a set 34°F temperature on a 77°F day), we need to know the thermal delta between the inside and outside of the fridge. (I’ll use 34°F for a good refrigeration value, and 77°F for the exterior temperature).
I’ll also use the average value of the interior and exterior surface area ((2.61+8.1) / 2) = 5.36 sq ft for this calculation. As a reminder, the equation to calculate heat loss in BTU/h is:
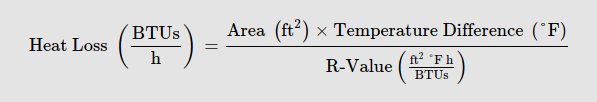
In imperial measurements:
[5.36 * (77-34) ] / 17 = 13.55 BTU/h
13.55 BTU/h divided by 3.41 = 3.97 watts
Using the SI system with things translated appropriately gives similar numbers:
0.49796 (25-1) / 2.99 = 3.99 watts
Of course, the above numbers may be completely incorrect, so I also did an experiment after building the cooler:
At 4:45pm I placed 3 refrigerated 12oz (355ml) cans of generic Dr. Pepper in my homemade DIY cooler with a temperature of 3.8°C. [The active TEC elements were turned off, as I was just testing the insulation properties.]
At 4:21am the next day (11 hours 36 minutes later, rounded to 11.5 hours hereafter) I opened the cooler and one can, measuring the interior temperature at 14.6°C. [we’ll assume all three cans gained the same amount of heat…I only wanted to drink one can.]
So, 36 fl oz (1065 ml) of (basically) water gained enough energy to raise its temperature 10.8°C in 11.5 hours. The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g-K. 1065ml = 1065 grams of water, or just about 1 kg. Nice how that works out.
4.184 J/g-C * 1065 g * 10.8 C = 48124.3680 Jules = 48.124 kJ = 0.0134 kWh = 13.4 Watt/hour
13.4 wh / 11.5 h = 1.1652173913 watts of continuous energy transfer from the outside to the inside of my cooler (heat gain, or cold loss).
You might notice that the calculated 3.9 watts is not equal to the observed 1.16 watts.
The main reason for this is that the interior of my cooler was never at 34 °F. It started at 3.8°C (39°F) and then raised up to 14.6°C (58°F) over 11.5 hours. It spends more time a higher temperatures, as the rate of heat transfer decreases as the thermal delta decreases. [Also, the ambient temperature was closer to 71.6°F, so the difference between the interior and the exterior was significantly smaller than in my previous calculations.]
For example:
[5.36 * (71-39) ] / 17 = 10.09 BTU/h / 3.41 = 2.95 watts
[5.36 * (71-58) ] / 17 = 4.099 BTU/h / 3.41 = 1.20 watts
However, the integration of the above numbers over 11.5 hours would still give me more heat loss than I observed. So either my experimental measures had a flaw, or the R value of my cooler is higher than the estimated 17.
However, as the results are of the right order of magnitude (4 watts vs 1.1 watts), I’m happy with my calculations and the experiment, and feel that the 4 watts of cooling power needed to maintain a 34°F interior temperature is a good upper bound on the performance needed by my TEC system to maintain temperature.